For decades, the "Dead Zone" has been the nightmare of every traveler, hiker, and rural resident in the USA. But as we move through 2026, that nightmare is officially over. With the full deployment of SpaceX's Direct to Cell satellites, your smartphone is no longer tethered to a physical tower on the ground. Starlink satellite calls on mobile phones have transformed every square inch of the planet into a reachable cellular zone, using nothing more than the device already in your pocket.
"In my 2 years of engineering 5G backhauls, I've never seen a shift as seismic as the 'Cell Tower in the Sky.' Starlink's V2 satellites act as orbital eNodeBs, broadcasting LTE signals directly to unmodified phones. This isn't traditional satellite internet; it is a seamless integration of anycast routing and orbital physics that makes 'No Service' a relic of the past."
1. Direct to Cell: The 2026 Cellular Breakthrough
Starlink satellite calls are powered by a technology called "Direct to Cell." Unlike the standard Starlink service that requires a "Dishy" and a Starlink Static IP, this service uses the existing LTE hardware inside your iPhone or Android device.
The 2026 Technical Logic:
SpaceX has equipped its latest satellites with an advanced de-modem that mimics a terrestrial cell tower. When you enter a region with no ground towers, your phone identifies the satellite signal as an extension of your carrier’s network (like T-Mobile in the USA).
Crucially, this uses Anycast Routing logic to ensure your call is always handed off to the satellite with the best line-of-sight, preventing dropped calls during orbital transits.
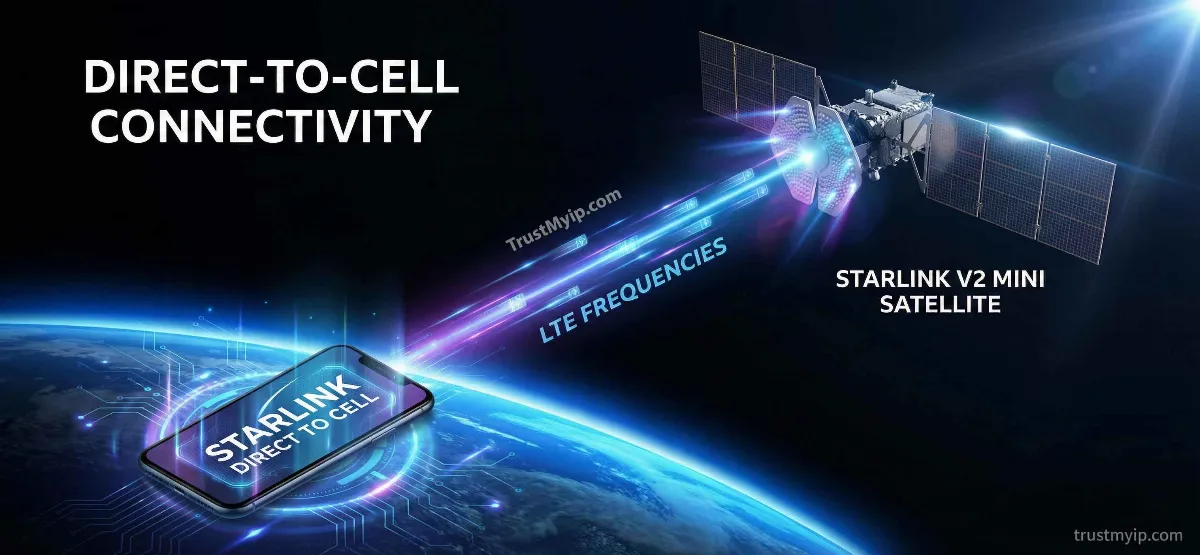
2. How Starlink Satellite Calls Work: The Orbital eNodeB
To understand how satellite calls on mobile phones work, we must look at the network path. In 2026, the satellite acts as a transparent bridge between your phone and the carrier's core network on the ground.
The Uplink (Phone to Space)
Your phone transmits at standard LTE frequencies. The Starlink satellite, positioned in Low Earth Orbit (LEO), captures this weak signal using a massive, sensitive antenna array.
The Backhaul (Space to Ground)
The satellite then relays your voice or text data via laser links to a Starlink Ground Station, which plugs directly into your mobile carrier's backend.
Pro Tip: Because the data travels to space, there is a minor delay. Read our Latency vs. Bandwidth Guide to understand how RTT affects satellite voice quality.
3. Performance Metrics: Terrestrial Tower vs. Starlink Satellite
While Starlink provides global coverage, the throughput and latency differ from your standard 5G tower in the city.
| Metric | Standard Cell Tower | Starlink Direct to Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Latency (Ping) | 10ms - 30ms | 50ms - 200ms |
| Bandwidth | High (Gbps per tower) | Low (Mbps per beam) |
| Compatibility | Any Mobile Phone | Standard LTE/4G Phones |
4. Do I Need a New Phone for Starlink Satellite Calls?
One of the greatest advantages of network bridging in space is that it requires zero hardware upgrades for the user. If your phone supports LTE (4G), it can technically talk to a Starlink satellite.
Carrier Support
In the USA, T-Mobile is the lead partner. Other global partners include Optus (Australia), Rogers (Canada), and Salt (Switzerland).
Device Logic
The phone sees the satellite as a standard roaming partner. No special apps or MAC address modifications are needed.
Curious about your phone's identity? Use our MAC Lookup Tool to see your network card's manufacturer details.
5. The Challenges of Starlink Mobile Connectivity
Despite the 2026 advancements, Starlink satellite calls are still bound by the laws of physics. Understanding these technical constraints is vital for reliable communication in remote areas.
- Line of Sight: Satellite calls require a clear view of the sky. Thick foliage or canyons can cause packet loss and drop your voice connection.
- Indoor Limitations: Unlike terrestrial 5G, satellite signals struggle to penetrate deep into buildings. For indoor use, you still need a traditional Intranet or Wi-Fi setup.
- Congestion: A single satellite beam covers a massive area. If thousands of authorized users try to call at once, the throughput per user drops, leading to poor audio quality.
6. Starlink Mobile IP Addressing: How Identity is Managed
When your phone connects to Starlink, it doesn't get a Starlink IP in the same way a home dish does. Instead, it maintains its carrier identity.
The satellite acts as a transparent relay. Your public data and IP address are still managed by your carrier’s DHCP allocation system on the ground. This ensures that features like iMessage and WhatsApp work without needing to re-authenticate your account. For a deep-dive into how Starlink manages its own internal pool, read our Starlink IP Addressing Guide.
Satellite Mobile FAQ
Do I need to be a Starlink subscriber to make calls?
No. You only need to be a subscriber of a partner carrier (like T-Mobile). The satellite calls are bundled into your existing mobile plan as a premium or standard "Global Coverage" feature.
What is the difference between Starlink Direct to Cell and Emergency SOS?
Apple's Emergency SOS is for emergencies only and is very slow (text-only). Starlink Direct to Cell is for standard voice, text, and basic data for everyday use.
Will satellite calls drain my battery?
Slightly more than a standard tower. Because the phone has to boost its transmission power to reach the satellite, you may see a 10-15% increase in battery drain during active calls.
Conclusion: The End of Global Isolation
Mastering the knowledge of Starlink satellite calls on mobile phones is to witness the final bridge in global telecommunications. In 2026, the distinction between "Urban" and "Wilderness" has blurred, as every smartphone becomes a satellite-capable device. By understanding the network latency, hardware logic, and anycast routing that powers this constellation, you can stay connected no matter where your journey takes you.
Audit Your Connection
Is your satellite link secure and performing at its peak? Use our forensic toolkit to audit your IP, check for DNS leaks, and analyze your network latency in one click.