Whether you are running a remote homestead in Montana or a high-tech startup in London, Starlink has revolutionized global connectivity. However, for many "Power Users," the honeymoon ends when they realize they can't access their home security cameras or host a Minecraft server. The culprit? CGNAT (Carrier-Grade NAT). In 2026, mastering the Starlink static IP architecture is the only way to transform your satellite connection from a basic web-browsing tool into a full-scale professional infrastructure.
"In my years of auditing SpaceX-level satellite flows, I've found that 95% of Starlink Residential users are trapped behind a private IP pool. Unlike traditional fiber, Starlink shares one Public IP with thousands of users. If you need a Static assignment for authorized users or remote access, you must shift to a 'Priority' plan or build a VPN tunnel to bypass the satellite gateway."
1. Starlink IP Architecture: The CGNAT Wall
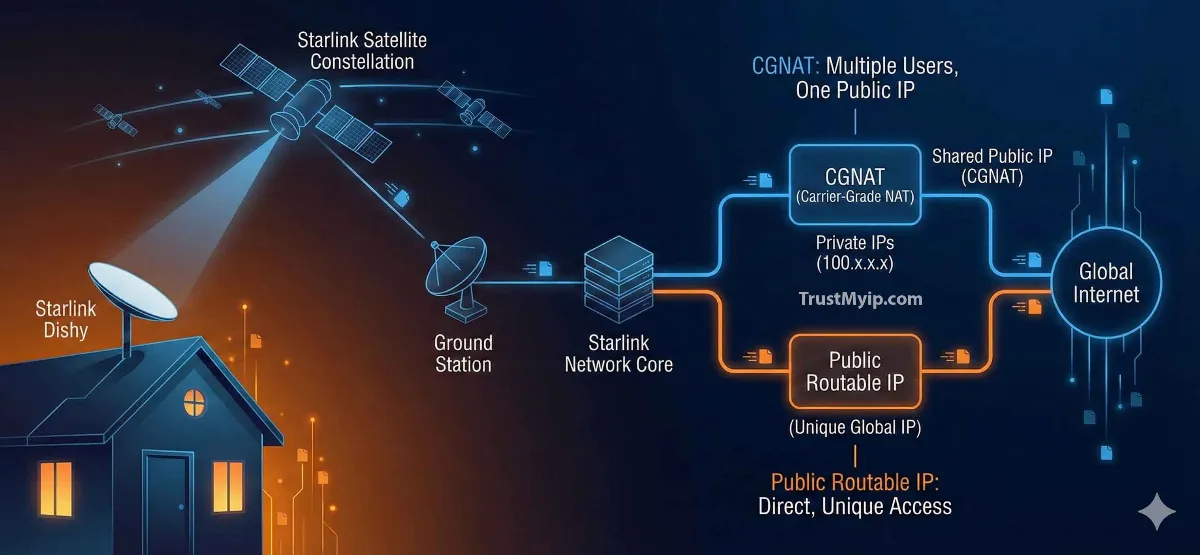
To understand how to get a Starlink static IP, you first need to know why you don't already have one. Starlink uses a technology called Carrier-Grade NAT (CGNAT) to conserve its limited pool of IPv4 addresses.
The CGNAT Reality
Your router configuration receives a private address (usually starting with 100.x.x.x). This address is invisible to the outside world, making traditional port forwarding impossible.
The Static Need
A Static IP provides a permanent, routable identity. This is required for hosting websites, VPN servers, or accessing your network inventory remotely.
Step 0: Audit Your Identity. Use our Starlink IP Lookup Tool to see if your IP starts with 100.x.x.x (CGNAT) or a true public range.
2. Starlink Residential vs. Business: Who Gets a Static IP?
The most official way to get a Starlink static IP is to upgrade your service plan. SpaceX has strictly segmented their network access control based on user tiers.
| Service Plan | IP Type | Routability | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Residential | CGNAT (Private) | Non-Routable | Streaming & Browsing |
| Business / Priority | Public Routable | Dynamic/Static Option | Hosting & Enterprise |
| Maritime / Mobility | Public Routable | High (Multi-region) | Global Travel |
3. Method 1: The Official Business Upgrade (Starlink Priority)
If you are on the Starlink Business (Priority) plan, you have the option to enable a "Public IP." While it is technically dynamic (it may change occasionally), it is fully routable, meaning port forwarding will finally work.
The Setup SOP:
1. Access your Starlink Account Dashboard via a web browser.
2. Navigate to Service Plan > Manage > IP Type.
3. Select Public IP. Your dish will reboot and request a routable DHCP allocation.
4. Pro Tip: Use an external router in Bypass Mode to manage your authorized users more efficiently.
4. Method 2: Bypassing CGNAT Without a Business Plan
Can't afford the Business plan? You can still change your identity by using a VPN tunnel with a dedicated IP. This effectively creates a "bridge" from a cloud server back to your Starlink dish.
Option A: Tailscale / ZeroTier
These are Software-Defined Networks (SDN) that allow you to connect your iPhone or Mac to your home Starlink network without needing a Static assignment or port forwarding.
Option B: VPS Tunneling
Rent a cheap $5/mo VPS in New York or London with a Static IP. Create a VPN tunnel (WireGuard) between the VPS and your Starlink router. Now, all your traffic uses the VPS's static identity!
Want to see how your VPN tunnel affects performance? Run our Starlink Latency Test to measure your RTT through the tunnel.
5. The Role of Starlink Bypass Mode in IP Management
If you are a Senior Infrastructure Architect, you know the stock Starlink router is limited. To gain full control over your network access control, you must enable Bypass Mode.
- What it does: Disables the built-in Wi-Fi and routing, passing the Public IP (or CGNAT IP) directly to your own high-end hardware.
- Why do it? Allows you to follow our Router IP Master Guide to implement MAC cloning or advanced firewall rules for your network documentation.
6. IPv6 on Starlink: Is it the "Free" Static IP?
While Starlink IPv4 is heavily NAT'ed, their IPv6 implementation is often publicly routable. This could be your ticket to how to resolve ip address conflict issues and remote access for free.
| IP Version | Starlink Implementation | Routability Status |
|---|---|---|
| IPv4 | CGNAT (Shared) | Blocked for Inbound |
| IPv6 | Native /64 Prefix | Publicly Routable |
Curious about your hardware identity? Use our MAC Address Auditor to identify your Starlink Dishy manufacturer and OUI.
7. Troubleshooting: Why can't I access my Starlink IP remotely?
If you've upgraded to Business or set up a VPN tunnel but still can't connect, you might be facing these technical constraints:
- DNS Resolution Latency: Satellite networks have inherent latency. Your DNS lookup might time out before the connection is established. Always use Cloudflare (1.1.1.1) for Starlink setups.
- IP Conflict with WAN: If you are using an external router, ensure its LAN IP (e.g., 192.168.1.1) doesn't clash with the Starlink dish's management IP (192.168.100.1). Learn more in our IP Conflict Fix Guide.
- Bypass Mode Failure: Sometimes Bypass Mode fails to release the DHCP lease. You may need to follow our Router IP Reset steps to force a new handshake.
Starlink IP FAQ
Does Starlink Residential provide a static IP?
No. Starlink Residential uses CGNAT. You get a private IP address that is shared with others. To get a routable IP, you must use a VPN tunnel or upgrade to a Priority plan.
Will a static IP improve my Starlink Ping?
Not directly. Latency on Starlink is caused by satellite distance and atmospheric interference. However, a static IP prevents "session drops" during IP changes, making gaming more stable.
What is the difference between a Starlink IP and a VPN IP?
Your Starlink IP is your physical identity assigned by SpaceX. A VPN IP is a logical mask. Learn more in our Stealth IP Guide.
Conclusion: Reclaiming Satellite Sovereignty
Navigating the Starlink static IP landscape in 2026 requires a mix of infrastructure upgrades and technical creativity. Whether you choose to invest in a Starlink Business priority plan or implement a high-speed VPN tunnel to bypass CGNAT, you are taking a critical step toward professional-grade connectivity. By auditing your network documentation and understanding the difference between a MAC address and an IP address, you ensure that your satellite link is as stable as any urban fiber connection.
Is Your Satellite Link Leaking?
Changing your Starlink settings is only half the battle. Use our forensic toolkit to audit your DNS, detect Proxy leaks, and check your satellite's reputation in one click.