In the intricate architecture of the modern internet, domain names like google.com are merely human-friendly masks for numeric identities. To a computer, a website is a numeric IP address. Whether you are troubleshooting a corporate security firewall, managing network documentation, or trying to stabilize your Hypixel gaming connection, knowing how to find the IP address of a website using CMD is a critical forensic skill. In 2026, as websites adopt complex Anycast Routing and global CDNs, a simple ping is often not enough. You need a multi-layered approach to unmask the true destination of your data packets.
"In my 20 years of auditing global networks, I've seen many administrators rely on outdated lookup methods. A hostname in 2026 can resolve to dozens of IPs depending on your network path. If you don't understand how to force a DNS Resolution through specific name servers using the Command Prompt, you are only seeing half the picture."
1. The Logic of IP Resolution: From Hostname to Layer 3
Before we dive into the commands, it is vital to understand the TCP/IP stack. When you use the command prompt to find the IP address of a website, you are triggering a request to a Recursive DNS Resolver.
Anycast vs. Dedicated IPs
Major platforms use Anycast Routing to ensure that a user in the USA and a user in Europe receive the fastest throughput by hitting the nearest geographic node. This is why the numeric IP you find via CMD today might be different from the one you find tomorrow.
Step 0: Identity Check. Before querying a remote site, verify your own status. Use our Public IP Identity Tool to see your current ISP and gateway location.
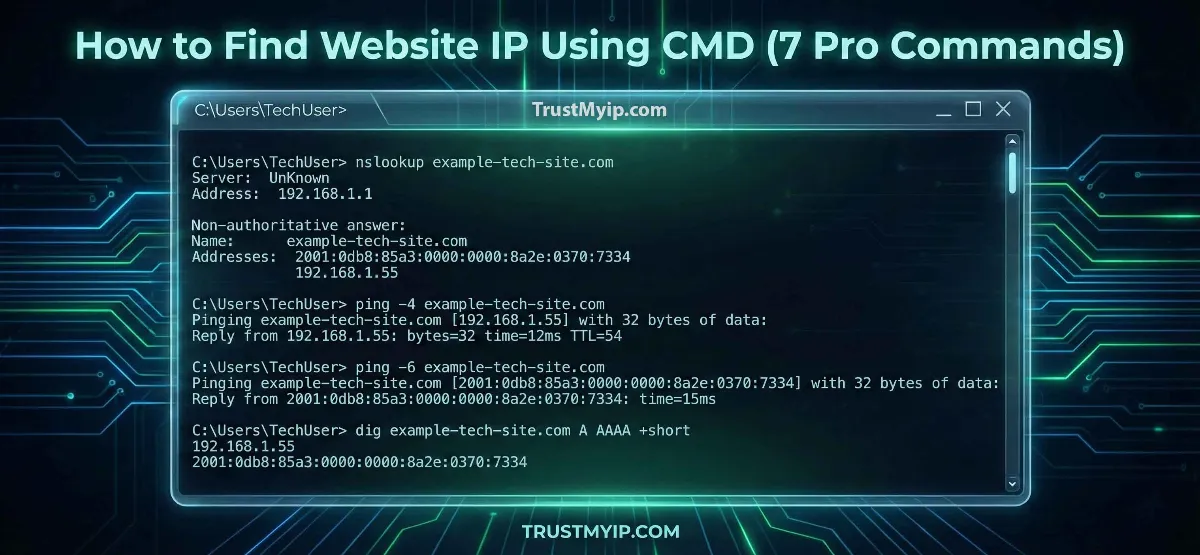
2. Method 1: The PING Command (The Quick Diagnostic)
The most common command to find the IP address of a website is ping. While its primary purpose is measuring latency, it also performs an immediate DNS lookup.
Command Syntax:
ping target-website.com
Advanced Ping Flags for 2026
-
01
Force IPv4:
ping -4 target.comMany 2026 networks prefer IPv6. Use this flag if you specifically need the older 32-bit numeric IP for corporate security filters.
-
02
Continuous Ping:
ping -t target.comUseful for identifying IP conflicts or periodic connection drops. Press Ctrl + C to stop the process. Read our IP Conflict Manual for more depth.
3. Method 2: NSLOOKUP (The Professional Standard)
If a website’s firewall blocks ICMP (Ping) requests, your ping will return a "Request Timed Out." To get the IP address of a website using CMD without hitting the server directly, you must use nslookup.
Interactive Mode vs. Non-Interactive
Typing nslookup by itself enters interactive mode, allowing you to query different DNS Resolution records (A, AAAA, MX, TXT).
The Forensic Audit Procedure
1. Open CMD and type nslookup.
2. Type server 8.8.8.8 to use Google's DNS instead of your ISP's.
3. Type the domain name (e.g., apple.com).
4. The command will return all numeric IPs associated with that domain, including secondary CDN nodes.
4. Method 3: TRACERT (Identifying the Gateway)
Sometimes the final IP isn't as important as the network path it takes to get there. The tracert command shows you every "Hop" between your Windows PC and the target.
When you run tracert google.com, the very first line after the hostname resolution will show you the destination's Public IP. This is extremely helpful for identifying if your traffic is being rerouted through a VPN tunnel or a malicious proxy. For a comparison of these identities, read our VPN vs. Proxy Forensic Guide.
Seeing high latency in your trace? Measure the impact using our Advanced Ping Test Tool.
5. Method 4: Resolve-DnsName (PowerShell Modernization)
For authorized users on Windows 10 or 11, PowerShell offers a much more detailed DNS Resolution command than the traditional CMD.
Resolve-DnsName -Name target-website.com
This command provides a detailed table including the TTL (Time to Live), Section, and specific Record Type (A for IPv4, AAAA for IPv6). It is the preferred method for network inventory and documentation in 2026.
6. Why Do I See Multiple IP Addresses?
When you use the command prompt to get the IP address of a website like facebook.com, you will often see a list of 5 to 10 different addresses. This is not an error; it is a load-balancing strategy.
| Architecture | IP Behavior | Primary Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Dedicated Server | One Static IP | Small Websites / Private Blogs |
| CDN (Cloudflare/Akamai) | Multiple Regional IPs | High Throughput & Speed |
| Anycast Routing | Dynamic Geo-IPs | Failover Protection |
Using Starlink? Satellite users hit specific ground stations that change their resolved IPs frequently. Learn why in our Starlink IP Architecture Guide.
7. Troubleshooting: "Unknown Host" and Cache Issues
If your command to find IP address of website fails with a "Non-existent domain" error, you might be dealing with a DNS Resolution cache issue or a stale entry.
The Forensic Fix List:
-
Flush DNS Cache: Your OS remembers old IPs. Run
ipconfig /flushdnsto force a fresh lookup. See our IP Not Found Resolution Manual. - Verify Subnet Status: If you have an IP Address Conflict on your local LAN, outbound DNS requests may time out. Follow our Conflict Fix Guide.
- Check MAC Address Bindings: In some corporate security setups, your hardware identity affects your DNS path. Understand the Difference Between MAC and IP.
Conclusion: Controlling Your Network Identity
Mastering how to find the IP address of a website using CMD is the foundation of digital literacy in 2026. Whether you use the speed of ping, the forensic detail of nslookup, or the modern power of Resolve-DnsName, you are reclaiming control over your network path. By auditing your DNS Resolution, understanding the Anycast Routing nodes of major CDNs, and clearing your local cache, you ensure that your connection to the World Wide Web remains reachable, resilient, and secure.
Is Your DNS Secure?
Finding the IP is just the beginning. Use our forensic toolkit to audit your DNS health, detect Proxy leaks, and verify your 2026 IP reputation in one click.