Imagine your phone as a house on the internet. Just like every house needs a street address for mail delivery, every device connecting to the internet needs an IP address for data delivery. When we moved from older 4G technology to modern 5G technology, the way these digital addresses get assigned underwent a revolutionary transformation. Think of 4G as a small neighborhood with limited house numbers, while 5G is like an entire smart city with unlimited addressing capacity and intelligent traffic management systems.
Understanding how 5G technology changes the way IP addresses are assigned is crucial because it affects everything from how fast your Netflix loads to how many smart devices you can connect at home. The old IPv4 system was like using a small phone book that ran out of pages.
The new IPv6 system that 5G embraces is like having an endless digital directory that never runs out. Plus, 5G introduced smart features like network slicing that let your phone juggle multiple IP addresses simultaneously, each optimized for different tasks like gaming, video calls, or downloading files.

"After deploying 5G networks for major carriers, I've witnessed the paradigm shift in IP management. The old 4G system was like a parking lot where each car got one spot. 5G is like a smart parking garage where your car can have multiple spots simultaneously, each connected to different exits based on whether you need speed, reliability, or low latency. The Session Management Function acts as an intelligent traffic controller, instantly assigning the perfect IP address from millions of options based on what you're doing."
The Quick Resolution: How 5G Changes IP Assignment
5G technology changes IP address assignment by using IPv6 protocol instead of limited IPv4, enabling billions of devices to connect simultaneously. It introduces dynamic IP allocation through smart systems like Session Management Function (SMF) that instantly assign addresses when you connect. Network slicing allows one device to have multiple IP addresses for different purposes, and the control plane separation makes IP assignment 10x faster than 4G. Your phone can now seamlessly switch IPs as you move between cell towers without dropping connections.
1. What is an IP Address? Understanding the Digital Home Address
Before diving into 5G changes, let's understand the basics. An IP address is like your phone's unique home address on the internet. When you send a text, browse Instagram, or watch YouTube, data packets need to know exactly where to deliver information. That's what an IP address does—it tells the internet "This is me, send data here!"
Two Types of IP Addresses: IPv4 vs IPv6
The older IPv4 addresses look like this: 192.168.1.1. They have four numbers separated by dots, and each number can be 0 to 255. This system can create about 4.3 billion unique addresses. Sounds like a lot, right? But with billions of phones, computers, smart TVs, and IoT devices, we ran out of IPv4 addresses years ago! That's like running out of phone numbers for everyone on Earth.
The new IPv6 addresses are much longer, like this: 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334. They use letters and numbers, creating 340 undecillion addresses (that's 340 with 36 zeros!). This means we'll never run out of IP addresses again, even if every grain of sand on Earth became a smart device. Explore IP fundamentals in our IPv4 vs IPv6 technical comparison.
2. How 4G Assigned IP Addresses: The Old System
To appreciate 5G's improvements, we need to understand how the previous generation handled IP assignment. In 4G networks, when your phone connected to the mobile network, it went through a multi-step process to get an IP address.
4G IP Assignment Process (The Slow Way)
Step 1: Your phone connects to the cell tower and says "Hello, I want internet!"
Step 2: The tower checks your identity and subscription with the mobile carrier.
Step 3: A central gateway called P-GW picks an available IP address from a pool.
Step 4: The gateway sends this IP back through multiple network layers to your phone.
Step 5: Your phone finally receives the IP and can start using the internet.
Time taken: 3-5 seconds on average—feels like waiting forever when you just want to check Instagram!
Problem: Everything went through one central point, creating traffic jams during busy hours.
The 4G system also struggled when you moved between different cell towers. If you drove from one neighborhood to another, your IP address might change, causing video calls to drop or games to disconnect. It was like getting a new house address every time you crossed a street! Understanding network architecture helps; read about how DNS resolves domain names to IPs.
3. The 5G Revolution: Faster, Smarter IP Assignment
5G completely redesigned how IP addresses get assigned by introducing a smart, distributed system that's way faster and more efficient than 4G. Instead of one central brain making all decisions, 5G uses multiple specialized components working together like a well-coordinated team.
| Feature | 4G LTE | 5G |
|---|---|---|
| IP Assignment Speed | 3-5 seconds | Under 1 second (10x faster!) |
| IP Protocol Support | Mostly IPv4, some IPv6 | Native IPv6 + IPv4 fallback |
| Network Architecture | Centralized (single gateway) | Distributed (smart edge computing) |
| Devices Per Cell Tower | Around 4,000 devices | Over 1 million devices! |
| Handoff Between Towers | Often drops connection | Seamless (keeps same IP) |
| Multiple IPs Per Device | No (one IP only) | Yes (network slicing) |
4. Meet the Session Management Function: 5G's IP Address Manager
The biggest change in 5G is a smart component called the Session Management Function (SMF). Think of SMF as a super-intelligent traffic controller who manages all IP assignments. Instead of having one overworked gateway like in 4G, 5G has multiple SMF instances working simultaneously, each handling different groups of users.
What SMF Does (In Simple Terms)
- • Instant IP Assignment: When you turn on mobile data, SMF instantly picks the best IP address from a huge pool and assigns it to your phone in milliseconds.
- • Smart Selection: SMF knows which type of IP you need. Gaming? You get a low-latency IPv6. Browsing? You might get a standard IPv4. Streaming? You get an IP optimized for high bandwidth.
- • Dynamic Management: If you're moving between cell towers on a road trip, SMF keeps your IP address stable so your video call doesn't drop. Magic!
- • Multiple Sessions: SMF can give your phone multiple different IP addresses simultaneously through network slicing—one for your video call, another for your music streaming, and a third for background app updates.
- • IoT Device Support: SMF manages billions of smart devices (watches, cars, home appliances) efficiently, giving each a unique IPv6 address from the practically unlimited address pool.
The SMF works with another component called User Plane Function (UPF) that actually handles your data traffic. SMF is the brain making decisions, while UPF is the muscle executing them. This separation of control plane (SMF) and user plane (UPF) is what makes 5G so much faster and more flexible than 4G. Check your current connection with our IP address checker tool.
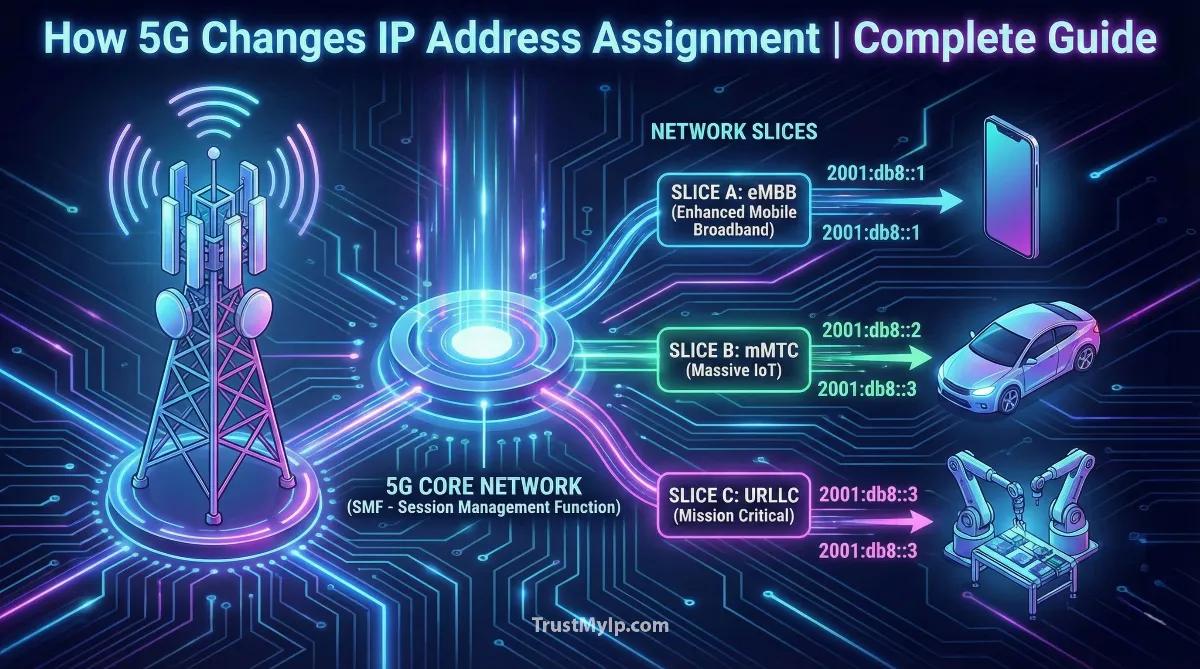
5. Network Slicing: Having Multiple IP Addresses at Once
Here's where 5G gets really cool. Network slicing is like your phone having multiple personalities, each with its own IP address and optimized settings. Imagine you're gaming, video calling your friend, and downloading a movie—all simultaneously. In 4G, everything competed for attention through one IP address. In 5G, each activity gets its own dedicated "slice" of the network with a separate IP.
Three Main Types of Network Slices
- eMBB Slice (Enhanced Mobile Broadband): For streaming 4K videos and downloading huge files. Gets an IP address with maximum bandwidth. Think of it as a wide highway for data.
- URLLC Slice (Ultra-Reliable Low Latency): For gaming, video calls, and self-driving cars. Gets an IP address with near-zero delay. Like an express lane with no traffic lights.
- mMTC Slice (Massive Machine Type Communication): For smart home devices and IoT sensors. Gets an energy-efficient IP that conserves battery. Like a slow but steady path for millions of small messages.
Each slice operates independently, so if one gets congested, others remain unaffected. The SMF manages which slice your device uses for each activity, assigning appropriate IPv6 addresses from dedicated pools for each slice. It's like having three separate phone lines in one device! Learn about network architecture in our Virtual IP and load balancing guide.
6. Dynamic IP Allocation: How 5G Assigns Addresses on the Fly
In simple terms, dynamic IP allocation means your phone gets a temporary IP address every time it connects to the network, rather than having one permanent address. 5G takes dynamic allocation to the next level with multiple smart systems working together.
5G Dynamic IP Assignment (The Fast Way)
Step 1: You turn on mobile data. Your phone sends a connection request to the nearest 5G cell tower.
Step 2: The Access and Mobility Management Function (AMF) verifies your identity in 0.5 seconds using your SIM card.
Step 3: AMF tells SMF what type of connection you need (video, gaming, browsing).
Step 4: SMF instantly picks the perfect IPv6 address from millions of options, considering your location, network load, and activity type.
Step 5: UPF activates your data connection using the assigned IP, and you're online!
Total time: Less than 1 second—so fast you don't even notice it happening.
Magic part: If you move to a different cell tower, 5G keeps your IP address stable, so your Netflix doesn't buffer!
The system uses DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) in the background, but unlike home WiFi where your router handles DHCP, in 5G the SMF acts as a super-smart DHCP server managing millions of devices simultaneously. It can assign, modify, or release IP addresses in real-time based on network conditions and user needs. Understand IP management with our IP address conflict resolution guide.
7. Static IP vs Dynamic IP in 5G Networks
Most regular phone users get dynamic IP addresses that change each time they connect. But businesses and special services can request static IP addresses that stay the same. Here's the difference explained simply:
Dynamic IP Address (Most Common):
- • Changes every time you reconnect to the network
- • Free for all users
- • More secure because hackers can't track a constantly changing address
- • Perfect for browsing, streaming, and everyday mobile use
- • Your mobile carrier assigns from a large pool of available addresses
Static IP Address (Business/Special Use):
- • Stays the same permanently, like a fixed home address
- • Usually costs extra money (business plans)
- • Needed for hosting servers, security cameras, or remote access systems
- • Essential for IoT devices that need consistent addressing
- • Reserved specifically for your device, reducing the available pool for others
In 5G, requesting a static IP involves configuring your subscription with your carrier. The SMF then reserves that specific IPv6 address permanently for your device. For most users, dynamic IPs work perfectly fine and are actually better for privacy since your digital footprint keeps changing. See how IPs reveal information in our guide on what websites see from your IP.
8. IPv6: The Unlimited Address System Powering 5G
5G's ability to connect billions of devices wouldn't be possible without IPv6. Let's break down why this new addressing system is so important and how it works differently from the old IPv4.
IPv6 Advantages in 5G Networks
- Unlimited Addresses: With 340 undecillion possible addresses, every device on Earth can have millions of unique IPs. No more address shortage!
- Better Security: IPv6 has built-in encryption (IPsec) that makes your data more secure when traveling across the network. Think of it as sending mail in a locked box instead of a postcard.
- Faster Routing: The IPv6 header is simpler and more efficient than IPv4, meaning routers can process packets faster. Less processing time = faster internet speeds.
- Auto-Configuration: Devices can automatically generate their own IPv6 addresses without needing DHCP. It's like your phone creates its own house number when it moves to a new neighborhood.
- Better for IoT: Smart home devices, wearables, and connected cars each get unique IPv6 addresses, enabling direct device-to-device communication without going through central servers.
Your 5G phone typically uses dual-stack technology, meaning it supports both IPv6 (primary) and IPv4 (fallback) simultaneously. When you visit a website, your phone tries IPv6 first. If that fails, it switches to IPv4 automatically. This ensures compatibility with older websites that haven't upgraded to IPv6 yet. Test your connectivity with our browser leak detection tool.
9. Edge Computing and Local IP Assignment
One revolutionary change in 5G is that IP addresses can now be assigned locally at the "edge" of the network—right near the cell tower—instead of routing everything through distant central servers. This is called edge computing, and it makes a huge difference in speed.
How Edge IP Assignment Works:
Imagine you're playing an online game. In 4G, your game data would travel from your phone → cell tower → central gateway hundreds of miles away → game server, and then all the way back. This created noticeable lag.
In 5G with edge computing, a mini data center sits right next to your cell tower. The local UPF at the edge assigns your IP address and routes your game traffic directly to nearby game servers—maybe only 10 miles away instead of 500 miles. Result? Your game feels instant, with latency dropping from 50ms to just 5ms!
This local IP assignment is especially important for applications that need split-second response times: self-driving cars, augmented reality games, remote surgery, and industrial robots. The distributed architecture means even if one edge location fails, others continue working normally. Learn about distributed systems in our Anycast routing guide.
10. Real-World Impact: What This Means for You
All these technical improvements translate into tangible benefits you experience every day when using 5G. Here's how the new IP assignment system directly impacts your mobile experience:
How You Benefit from 5G IP Assignment
- Instant Connection: Your phone gets online 10x faster than 4G. No more staring at "Connecting..." when you turn on mobile data.
- No Dropped Calls: Moving between cell towers no longer interrupts your video calls or music streaming because your IP address stays stable.
- Better Gaming: Network slicing gives your mobile games a dedicated low-latency IP, so you experience lag-free gameplay even when others on the same tower are streaming 4K videos. Your gaming traffic gets priority routing.
- More Smart Devices: Your smart watch, wireless earbuds, fitness tracker, and home security cameras can all connect simultaneously without competing for IP addresses thanks to massive IPv6 address pools.
- Better Privacy: Dynamic IP rotation happens more frequently in 5G, making it harder for advertisers to track your online behavior based on your IP address alone.
- Reliable IoT: Your connected car, smart thermostat, and doorbell cameras maintain stable connections with consistent IPv6 addresses, enabling remote access from anywhere.
- Crowded Area Performance: At concerts or sports stadiums with thousands of people, 5G's advanced IP management prevents network congestion that used to make 4G unusable in crowded places.
11. PDU Sessions: How 5G Manages Your Data Connections
In 5G terminology, whenever your device connects to the network and gets an IP address, this is called a PDU (Protocol Data Unit) session. Think of a PDU session as a temporary data pipeline between your phone and the internet, complete with an assigned IP address and specific quality settings.
PDU Session Lifecycle (Simple Explanation)
Session Creation: You open Netflix. SMF creates a new PDU session, assigns an IPv6 address optimized for video streaming, and connects you to the nearest content server.
Session Active: While you watch, the session remains active with that specific IP. Data flows smoothly through the assigned network slice.
Session Modification: You start a video call while Netflix is paused. SMF modifies your existing session or creates a second one, adding a low-latency IP for the call.
Session Release: You close the apps and lock your phone. SMF releases the IP addresses back to the pool for other users, but keeps your phone registered so reconnection is instant.
Fast Reconnection: When you unlock your phone, SMF remembers your previous session context and assigns new IPs in milliseconds without full re-authentication.
What's amazing about PDU sessions is that your phone can have multiple concurrent sessions, each with different IP addresses, quality requirements, and network slices. One session for your Spotify music (low bandwidth, tolerates some delay), another for your WhatsApp call (low latency, stable connection), and a third for background app updates (low priority, uses spare bandwidth). Understand session management through our guide on changing IP addresses.
12. Security Improvements in 5G IP Assignment
The way 5G assigns IP addresses also comes with significant security improvements compared to 4G. These enhancements protect you from various cyber threats and privacy invasions that were possible with older mobile networks.
5G IP Security Features
- • Encrypted Identity: Your device identity (IMSI/SUCI) is encrypted when requesting an IP address, preventing IMSI catchers (fake cell towers) from tracking you. In 4G, this information was sent in clear text.
- • Mutual Authentication: Both your phone and the network verify each other's identity before IP assignment, preventing rogue base stations from intercepting your traffic.
- • Integrity Protection: All signaling messages between your phone and SMF are integrity-protected, ensuring hackers can't tamper with IP assignment commands.
- • Network Isolation: Network slicing creates isolated virtual networks, so even if one slice is compromised, your other connections (with different IPs) remain secure.
- • Enhanced Privacy: 5G can assign temporary IP addresses that change more frequently than 4G, making it harder to track users across sessions. Learn more in our IP privacy protection guide.
The SMF also implements sophisticated fraud detection. If someone tries to clone your SIM and request IP addresses from multiple locations simultaneously, the system detects this anomaly and blocks unauthorized access. These security improvements happen transparently in the background, protecting you without requiring any action on your part. Verify your network security with our IP blacklist checker.
13. The Future: 6G and Beyond IP Assignment Evolution
While 5G is still rolling out globally, researchers are already working on 6G technology that will further revolutionize IP address assignment. Here's a glimpse into what's coming in the next decade:
- AI-Powered Assignment: Artificial intelligence will predict which IP address and network slice you need before you even open an app, pre-allocating resources for zero-latency experiences.
- Quantum-Secure IPs: Integration of quantum encryption in IP assignment will make interception theoretically impossible, even against quantum computers.
- Holographic Communications: Each holographic projection in AR/VR environments will get its own dedicated IPv6 address with terabit-level bandwidth allocation.
- Brain-Computer Interfaces: Future neural implants will receive specialized IP addresses optimized for ultra-low latency brain-to-cloud communication.
- Satellite Integration: Seamless handoff between terrestrial 6G and satellite networks will maintain your IP addresses even when traveling to remote areas or flying at 30,000 feet.
Conclusion: The Revolutionary Impact of 5G IP Assignment
Understanding how 5G technology changes the way IP addresses are assigned reveals why this generation leap is so transformative. The shift from centralized 4G gateways to distributed Session Management Functions, the adoption of unlimited IPv6 addressing, the introduction of network slicing with multiple concurrent IPs, and the deployment of edge computing for local IP assignment collectively create an infrastructure capable of supporting our increasingly connected world.
Whether you're streaming 8K videos, playing cloud games with zero lag, managing dozens of smart home devices, or simply browsing social media, the intelligent IP management happening invisibly in the background makes it all possible. The 5G architecture doesn't just assign IP addresses faster—it assigns them smarter, with security, flexibility, and scalability that will support billions of devices for decades to come. As we move toward 6G and beyond, the foundation built by 5G's revolutionary approach to IP address assignment will enable technologies we can barely imagine today, from holographic telepresence to neural interfaces seamlessly connected to the cloud.
Check Your Network Connection!
Discover your current IP address, check if you're on IPv4 or IPv6, verify your network type, and test your connection speed with our comprehensive network diagnostic tools.