Every millisecond matters in competitive gaming. When you fire a shot in Call of Duty, execute a combo in Street Fighter 6, or land a headshot in Valorant, the difference between victory and defeat often comes down to how quickly your actions reach the game server. Behind this invisible infrastructure lies a sophisticated system that uses your IP address to determine which server hosts your match, who you play against, and ultimately, how responsive your gaming experience feels.
Understanding how game servers use your IP for regional matchmaking reveals the intricate dance between IP geolocation databases, latency prediction algorithms, and skill-based matchmaking (SBMM) systems that power modern multiplayer games. This forensic guide deconstructs the technical architecture behind regional server selection, explains why you sometimes connect to distant servers despite closer options, and provides actionable strategies to optimize your connection for the lowest possible ping in 2026.

"After analyzing matchmaking systems across dozens of AAA titles, I've observed that most players fundamentally misunderstand how their IP address influences server selection. It's not simply about geographic proximity. Modern matchmaking algorithms weigh real-time latency measurements, player population density, skill brackets, and even time-of-day patterns to determine optimal server placement. The IP address serves as the initial seed for these calculations, but the final routing decision involves far more sophisticated network intelligence."
The Quick Resolution: IP-Based Regional Matchmaking
Game servers use your IP address to query geolocation databases (like MaxMind GeoIP) that map your IP to a physical location. This location data determines your initial regional server pool, after which the matchmaking algorithm measures actual ping latency to nearby data centers, factors in player availability and skill ratings, then connects you to the optimal server. The entire process typically completes in under 10 seconds, though complex matchmaking can extend queue times significantly.
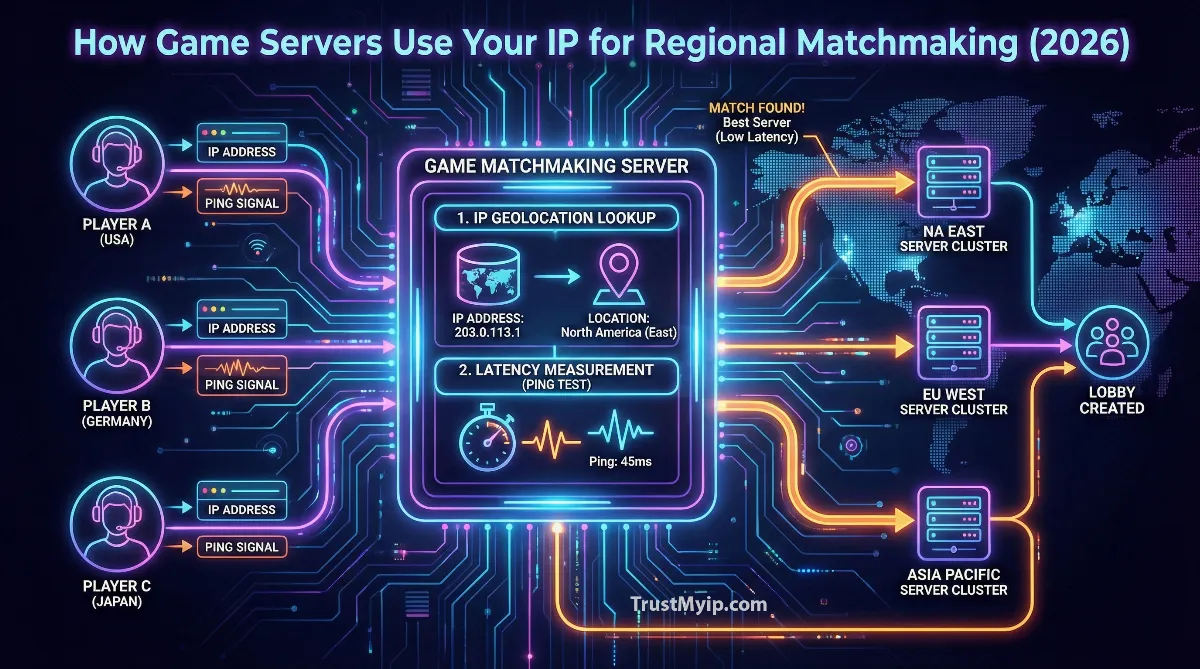
1. How IP Geolocation Powers Server Selection
The moment you launch a multiplayer game and click "Find Match," your gaming client initiates a connection to the game's matchmaking service. This backend system immediately captures your public IP address and queries an IP geolocation database to determine your approximate physical location. Understanding this process is crucial for anyone wanting to optimize their gaming experience.
The MaxMind GeoIP Standard
Most major game publishers rely on commercial IP geolocation services like MaxMind GeoIP2 or IP2Location to map player addresses to geographic coordinates. These databases maintain records for virtually every IP address block allocated worldwide, associating each with country, region, city, and approximate latitude/longitude coordinates. When Riot Games receives your connection request for Valorant, their servers query this database using your IP, receiving back data like "United States, California, Los Angeles, 34.0522, -118.2437" within milliseconds. For a deeper understanding of how IP addresses reveal location data, explore our guide on what information websites can see from your IP.
Accuracy Limitations of IP Geolocation
IP geolocation is inherently imprecise. MaxMind estimates approximately 80% accuracy at the state/region level within the United States, dropping to around 66% for city-level precision within a 50km radius. This imprecision explains why games sometimes route you to unexpected servers. Your ISP might route your traffic through infrastructure in a different city, causing the geolocation database to misidentify your location. Mobile network IPs present even greater challenges, as cellular towers may serve users across hundreds of kilometers while sharing IP address pools. Learn more about why your location might appear incorrect in our article on why your public IP shows a different city.
IP Geolocation Data Points Used in Matchmaking
Country Code: Determines which regional server cluster pool you enter (NA, EU, APAC, etc.).
Subdivision/State: Narrows selection to specific data centers within the region.
City Coordinates: Calculates estimated distance to each available game server.
ISP/ASN Data: Identifies your Internet Service Provider and autonomous system for routing optimization.
Connection Type: Detects whether you're on residential broadband, cellular, or corporate networks.
Timezone: Helps predict player activity patterns for queue time optimization.
2. The Matchmaking Pipeline: From IP to Game Server
Once your IP has been geolocated, the real matchmaking magic begins. Modern systems don't simply connect you to the nearest server; they orchestrate a complex multi-step process that balances latency, fairness, and queue times.
The typical matchmaking pipeline follows these sequential stages:
- • Stage 1 - IP Geolocation: Your public IP is mapped to geographic coordinates using commercial databases, establishing your initial regional pool.
- • Stage 2 - Latency Beaconing: Your game client pings multiple data centers in your region, measuring actual round-trip time (RTT) to each potential server location.
- • Stage 3 - Skill Bracket Assignment: Your matchmaking rating (MMR) or skill level filters the available player pool to find opponents of similar ability.
- • Stage 4 - Lobby Formation: The algorithm groups players who share acceptable latency ranges and skill brackets into a potential match.
- • Stage 5 - Server Deployment: A dedicated game server is either selected from available instances or dynamically spun up in the optimal location for all matched players.
Latency Beacons: Measuring Real-World Ping
While IP geolocation provides an estimate, actual network latency depends on countless variables: ISP routing policies, network congestion, submarine cable paths, and peering agreements between autonomous systems. To account for this, modern games implement latency beacon systems that actively measure your connection to potential servers. Fortnite, for example, displays ping values next to each matchmaking region in settings, updated in real-time as your client sends test packets to Epic's data centers worldwide. This measured latency, not the geolocated distance, ultimately determines which servers you can access. Check your current connection quality using our ping testing tool.
3. Regional Server Architecture: Where Game Servers Actually Live
Game publishers strategically deploy servers in major internet exchange points and cloud regions to minimize latency for the largest player populations. Understanding this infrastructure reveals why certain locations receive better connectivity.
| Region | Primary Data Centers | Coverage Area |
|---|---|---|
| North America East | Ashburn (Virginia), New York, Atlanta, Miami | Eastern US, Eastern Canada, Caribbean, parts of South America |
| North America West | Los Angeles, San Jose, Seattle, Dallas | Western US, Western Canada, Hawaii, Mexico |
| Europe | Frankfurt, London, Amsterdam, Paris, Madrid | Western Europe, Nordics, Eastern Europe, Middle East, North Africa |
| Asia Pacific | Singapore, Tokyo, Seoul, Sydney, Hong Kong | Southeast Asia, Japan, Korea, Australia, New Zealand, India |
| South America | São Paulo, Santiago, Buenos Aires | Brazil, Argentina, Chile, Colombia, Peru |
Frankfurt serves as Europe's gaming hub due to DE-CIX, the world's largest internet exchange with over 16 Terabits per second of peak traffic. Players from Spain to Turkey typically route through Frankfurt's data centers. Similarly, Ashburn, Virginia hosts the majority of North American game servers due to its concentration of fiber optic infrastructure and cloud provider presence. For players in geographically challenging locations like South Africa or parts of South America, this centralized infrastructure can mean 150ms+ baseline latency regardless of ISP quality. Understand more about how network routing affects your connection in our guide on network latency vs bandwidth vs throughput.
4. Skill-Based Matchmaking and Connection Quality
The intersection of skill-based matchmaking (SBMM) and regional server selection creates one of gaming's most debated systems. When Activision states "Ping is King" for Call of Duty matchmaking, they acknowledge that connection quality takes priority over skill brackets, but the reality involves complex tradeoffs.
Call of Duty Matchmaking Priority Hierarchy (Official)
- 1 Connection (Ping): The most heavily weighted factor. Players are matched based on proximity to data centers with the goal of minimizing latency. Low ping ensures responsive, fair gameplay.
- 2 Time to Match: Queue duration matters. The system loosens restrictions progressively to prevent excessive wait times, but connection constraints relax slower than skill constraints.
- 3 Skill/Performance: Your recent match performance influences lobby composition. The algorithm uses internal MMR calculations to group similarly skilled players.
- 4 Input Device & Platform: Controller vs. keyboard/mouse and console vs. PC factor into matchmaking for competitive fairness.
The Delta Ping Concept
Activision introduced the concept of Delta Ping in their matchmaking documentation, defining it as the difference between your best possible ping (to your nearest data center) and your ping to the server where your lobby is placed. The matchmaking algorithm "backs off" on skill restrictions faster than it loosens Delta Ping constraints. This means you're more likely to face opponents outside your skill bracket than to be placed on a high-latency server. However, during off-peak hours or in regions with smaller player populations, even ping constraints may expand to maintain acceptable queue times.
5. Why You Sometimes Connect to Distant Servers
Every gamer has experienced the frustration of connecting to servers far from their location despite closer options existing. Several technical and algorithmic factors cause this seemingly counterintuitive behavior.
Common reasons for distant server connections:
- • Incorrect IP Geolocation: Your ISP's routing infrastructure may cause geolocation databases to misidentify your location, placing you in the wrong regional pool entirely.
- • Player Population Imbalance: During off-peak hours in your region, the matchmaker may expand search to adjacent regions to reduce queue times.
- • Skill Bracket Scarcity: Very high or very low skill players have smaller matchmaking pools, sometimes requiring cross-region searches to find appropriate opponents.
- • Server Capacity Constraints: If nearby servers are at capacity, the system routes overflow traffic to servers with available slots, regardless of distance.
- • Party/Group Matchmaking: When playing with friends from different regions, the matchmaker selects servers that minimize total party latency, not individual latency.
- • ISP Routing Anomalies: Poor peering agreements between your ISP and game server hosting providers can make distant servers technically faster to reach.
The CDN and Load Balancer Factor
Many games route initial connections through Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) and load balancers that make routing decisions based on operational costs rather than pure latency optimization. A CDN might redirect your traffic through a longer path if it's cheaper for the provider, even when a shorter route exists. Additionally, game clients sometimes cache server IP addresses or region assignments, causing you to connect to previously optimal servers that no longer provide the best connection. Understanding how Anycast routing works can help explain why your traffic sometimes takes unexpected paths.
6. VPNs and Regional Matchmaking: The Reality
Using a VPN to change your apparent IP location for gaming has become increasingly popular, but the relationship between VPNs and matchmaking is more nuanced than simply "connect to Japan for easier lobbies."
How VPNs Affect Game Matchmaking
IP Geolocation Shift: Your IP appears to originate from the VPN server's location, potentially placing you in a different regional matchmaking pool.
Added Latency: VPN tunneling adds processing overhead and routing distance, typically increasing ping by 10-50ms depending on VPN server location.
Datacenter IP Detection: Many games use databases like MaxMind to detect VPN/proxy IPs and may block them or apply restrictions.
Latency Beacon Override: Even if your geolocated region changes, real-time ping measurements to game servers still occur, potentially revealing your true location.
Terms of Service Risks: Some publishers explicitly prohibit VPN use for matchmaking manipulation; violations can result in bans.
The effectiveness of VPNs for matchmaking manipulation varies dramatically by game. Titles that rely heavily on IP geolocation without secondary verification may be more susceptible, while games implementing robust latency beacon systems will detect the actual network path regardless of apparent IP location. For legitimate privacy-focused VPN use while gaming, check our comprehensive guide on VPN vs Proxy for hiding your IP.
7. Optimizing Your Connection for Better Matchmaking
While you cannot control game server locations or matchmaking algorithms, several actionable steps can ensure your connection is optimized for the best possible regional server assignment.
Connection Optimization Checklist
- Use Wired Ethernet: WiFi adds 10-30ms of latency and introduces packet loss. A Cat6 ethernet cable directly to your router eliminates wireless interference entirely.
- Enable QoS (Quality of Service): Configure your router to prioritize gaming traffic over downloads and streaming, ensuring your game packets receive preferential treatment.
- Manually Select Regions: Most games allow manual region selection in settings. Test each region's displayed ping and choose the consistently lowest option rather than relying on "Auto."
- Update Router Firmware: Outdated router firmware can contain routing bugs or suboptimal NAT handling that increases latency.
- Configure DNS Properly: Using fast DNS servers like Cloudflare (1.1.1.1) or Google (8.8.8.8) can improve initial connection times, though it won't affect gameplay ping directly. Learn about DNS in our DNS resolution guide.
- Close Background Applications: Windows Update, cloud sync services, and streaming apps consume bandwidth and can cause ping spikes during gameplay.
Verifying Your IP Geolocation
Before troubleshooting matchmaking issues, verify how your IP address is being geolocated. Game servers see your public IP assigned by your ISP, not your local network address. Use our IP lookup tool to see exactly what location data is associated with your current IP address. If the geolocation shows an incorrect city or region, this directly impacts which game servers you're assigned to.
8. Game-Specific Matchmaking Systems
Different games implement regional matchmaking with varying degrees of sophistication. Understanding how your specific game handles server selection can help set appropriate expectations.
| Game | Matchmaking Approach | Region Selection |
|---|---|---|
| Valorant | IP geolocation + active ping measurement. Strict regional pools. | Account-locked to region; requires support ticket to change |
| Fortnite | Real-time ping display per region. Auto or manual selection. | Freely changeable in settings menu |
| Call of Duty | Delta Ping system prioritizing connection over skill. | Automatic with max acceptable ping setting |
| League of Legends | Single centralized server per region (e.g., Chicago for NA). | Account-locked; requires new account for different region |
| CS2 | Max acceptable ping setting with server routing display. | Console command control over max matchmaking ping |
9. Troubleshooting Wrong Region Connections
If you consistently connect to servers outside your expected region, systematic troubleshooting can identify the root cause.
- Verify IP Geolocation: Use IP lookup services to confirm your IP's associated location matches your physical location. If incorrect, contact your ISP about IP block assignment.
- Clear Game Cache: Cached region assignments can persist even after network changes. Delete game configuration files to force fresh server discovery.
- Check for VPN/Proxy Interference: Ensure no system-level VPN or proxy is active. Some security software routes traffic through foreign servers unintentionally.
- Test During Peak Hours: Try matchmaking during your region's peak gaming hours when local server populations are highest, reducing cross-region matching likelihood.
- Monitor Actual Ping: Use in-game network statistics to verify actual server latency. If displayed ping doesn't match expected regional servers, routing issues exist.
10. The Future of Game Server Selection
Gaming infrastructure continues evolving with technologies that may fundamentally change how regional matchmaking operates. Edge computing deployments are bringing game servers closer to players than ever before, while network acceleration services like those from AWS Global Accelerator optimize routing paths in real-time. Some studios are experimenting with predictive matchmaking that pre-positions servers based on anticipated player activity patterns.
The rise of cloud gaming platforms like Xbox Cloud Gaming and NVIDIA GeForce NOW introduces additional complexity, as both player-to-cloud and cloud-to-gameserver latency must be optimized simultaneously. Meanwhile, Starlink and other satellite internet constellations are beginning to serve gamers in previously underserved regions, though with unique latency characteristics that traditional matchmaking systems weren't designed to handle. Learn more about satellite internet gaming in our Starlink performance guide.
Conclusion: Mastering Regional Matchmaking
Understanding how game servers use your IP for regional matchmaking reveals the sophisticated infrastructure that makes global multiplayer gaming possible. Your IP address serves as the initial data point for geolocation databases that determine your regional server pool, but the final matchmaking decision involves real-time latency measurements, skill-based algorithms, player population analysis, and server capacity considerations. While you cannot control these systems directly, optimizing your home network, verifying your IP geolocation accuracy, and understanding game-specific matchmaking behaviors empowers you to achieve the best possible connection quality. In competitive gaming where milliseconds determine outcomes, this knowledge transforms from technical curiosity into genuine competitive advantage.
Check Your Gaming Connection!
Verify your IP geolocation, test your ping to game servers worldwide, and diagnose network issues affecting your matchmaking experience with our professional toolkit.